Are Ants Blue?
Ants are fascinating creatures that play a vital role in our ecosystems. Found almost everywhere on Earth, they exhibit a wide range of colors, behaviors, and ecological functions. However, the question arises: Are ants blue? This article delves into the vibrant world of ants, exploring their colors, the science behind their pigmentation, and the intriguing phenomenon of blue ants.
Quick Info Table: Ant Coloration
| Ant Type | Common Colors | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| Carpenter Ant | Black, Brown | Known for nesting in wood |
| Fire Ant | Red, Brown | Aggressive, known for painful bites |
| Leafcutter Ant | Green, Brown | Famous for cutting leaves for fungus |
| Blue Ant | Iridescent Blue | Found in Australia, not true blue |
| Sugar Ant | Yellow, Black | Attracted to sweet substances |
Understanding Ant Coloration
The Science of Ant Colors
Ants can display a variety of colors, ranging from black and brown to red and even yellow. The coloration of ants is primarily due to pigmentation and the structural properties of their exoskeletons. Pigments such as melanin contribute to darker colors, while structural coloration can create vibrant hues by reflecting light in specific ways.
In addition to these pigments, some ants exhibit iridescence, a phenomenon where their colors change based on the angle of light. This is particularly noticeable in certain species, like the blue ants found in Australia.
Why Do Ants Have Different Colors?
The coloration of ants serves various purposes:
- Camouflage: Many ants are colored to blend into their environments, aiding in predator avoidance and improving their foraging success.
- Communication: Some colors can signal different roles within the colony or indicate the presence of threats.
- Thermoregulation: Darker ants may absorb more heat, which can be beneficial in cooler environments, while lighter colors reflect sunlight.
The Mystery of Blue Ants
Are There Truly Blue Ants?
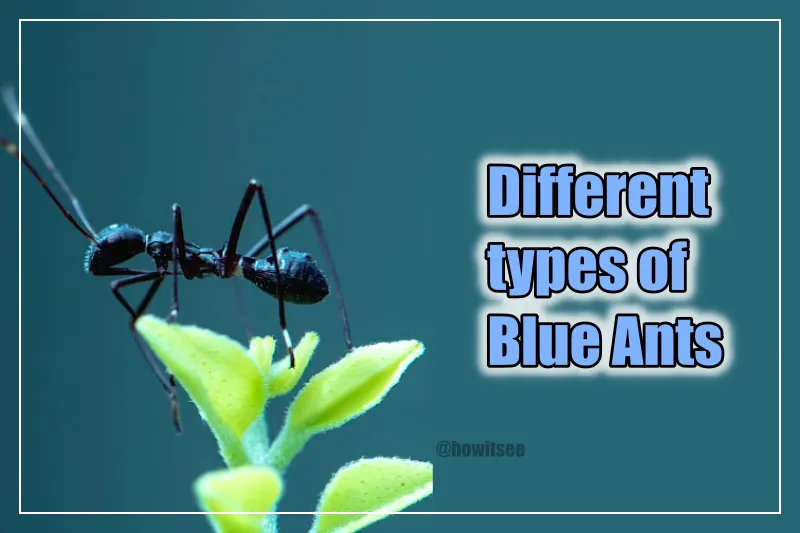
The term "blue ant" often leads to confusion. While there are ants that appear blue, they are not truly blue in the sense that they contain blue pigments. Rather, species such as the blue carpenter ant (Camarota) exhibit an iridescent quality that gives them a blue appearance.
These ants are predominantly black or dark in color, but the structural features of their exoskeleton reflect light in such a way that they can appear blue when viewed from certain angles. This optical illusion is similar to how a soap bubble or peacock feathers can show a range of colors.
The Blue Ants of Australia
Among the most notable examples of ants that appear blue are the blue ants found in Australia, specifically within the family Myrmecia. These ants are known for their vibrant coloration and are often referred to as "blue" due to their striking appearance. However, like other so-called blue ants, they are not truly blue on a microscopic level.
Fascinating Facts About Ant Colors
Color Variation Across Species
- Diversity: Over 12,000 species of ants have been identified, each exhibiting unique colors and patterns. This diversity plays a significant role in their survival strategies.
- Color Adaptations: In some regions, ants have adapted their colors based on environmental changes. For example, ants in shaded areas might be darker, while those in open, sunlit areas may be lighter to reflect heat.
Cultural and Ecological Significance
- Symbolism: In various cultures, ants are seen as symbols of hard work and community. Their colors can also play a role in cultural representations, with certain colors regarded as auspicious.
- Ecological Roles: Coloration can affect an ant's ecological role. For example, brightly colored ants may serve as warning signals to potential predators, indicating that they possess a nasty sting or taste bad.
The Role of Color in Ant Behavior
How Color Affects Interaction
Color can significantly influence the way ants interact with each other and their environment. For instance, researchers have found that certain colors can impact how ants recognize each other, which is crucial for maintaining colony cohesion.
- Recognition: Ants use chemical signals primarily to identify members of their colony, but visual cues from coloration can also play a role, especially in species that rely on sight for communication.
- Foraging: Brightly colored ants are often easier to spot by predators, leading to a balance between being visible for foraging and being hidden from threats.
The Impact of Environmental Changes
Environmental factors such as sunlight and temperature can influence the coloration of ants. For example, ants living in hotter regions may develop lighter colors to reflect sunlight, while those in cooler areas may become darker to absorb heat.
Conclusion: The Colorful World of Ants
In conclusion, while the question “Are ants blue?” may lead to intriguing explorations, it reveals much more about the diversity and complexity of the ant world. Ants showcase a remarkable array of colors due to pigmentation and structural features, with some species exhibiting blue-like hues through iridescence.
Understanding the role of color in ants not only enriches our knowledge about these small but mighty creatures but also highlights their ecological importance and adaptability. As we continue to study ants and their behaviors, we uncover the intricate ways in which they thrive in various environments.
Whether you're a casual observer or a serious entomologist, the colorful world of ants offers endless opportunities for discovery and appreciation. So next time you spot an ant, take a moment to observe its color and consider the fascinating science behind it!



Comments ()